New research published by SnapLogic, provider of a high-ranking Intelligent Integration Platform, reveals that 77% of IT decision-makers (ITDMs) don’t completely trust the data within their organisation for timely and accurate decision-making. With 98% of those surveyed reporting that data is reviewed and analysed on a weekly basis by teams across the enterprise, this data distrust should be cause for concern, potentially leaving organisations open to poorly considered decisions and misguided actions.
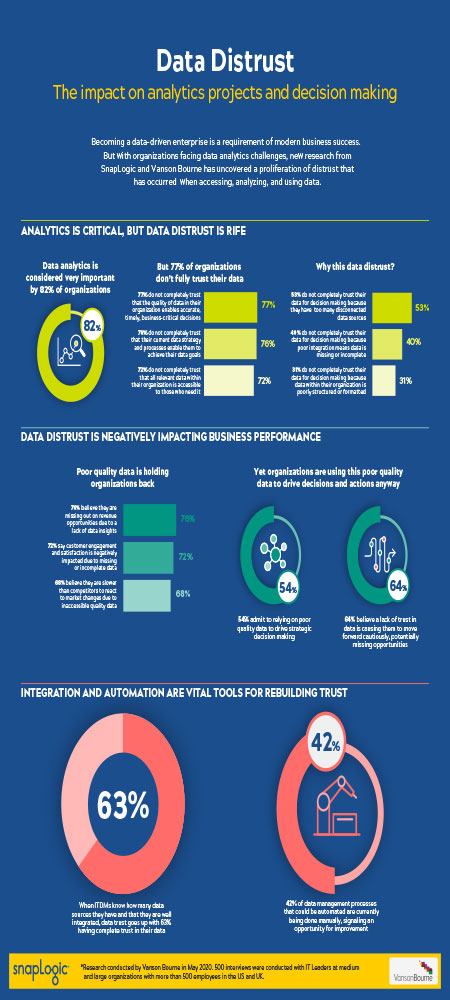
The new study, Data Distrust, conducted by independent research firm Vanson Bourne, found that the majority of this distrust in data comes down to ineffective or flawed data analytics processes. Despite the fact that data analytics is seen as very important for 82% of organisations, it’s almost become commonplace for data snags to impact results. In 84% of organisations, data analytics projects are delayed due to the data not being in the right format, while for 82% the data used is of such poor quality that analytics projects need to be reworked.
The distrust caused by these data issues has a significant impact on organisational success, with 76% reporting missed revenue opportunities, 72% stating customer engagement and satisfaction is negatively impacted and 68% believing they are slower than competitors to react to market changes.
Worryingly, those who have little or no trust in their organisation’s data report that 54% of strategic decisions continue to use that same data, risking flawed decisions and perhaps hindering, rather than helping, the business achieve their goals. Indeed, almost two-thirds (64%) of ITDMs believe a lack of trust in data is causing their organisation to move forward cautiously, in turn missing opportunities that may otherwise put them ahead.
Rebuilding trust in data and data analytics overwhelmingly comes down to improving the ease and speed of access to quality, decision-ready data within the organisation. When asked what was needed to improve data quality for analysis, respondents noted some key areas: better data cleaning and standardisation, modernisation of infrastructure and the integration of data silos. The latter was particularly important, as over half (53%) called out growing data siloes and inaccessible data as the biggest drivers behind their lack of trust.
“It’s well known that effective use of data analytics can provide significant business advantages. But to know that so many organisations are making business decisions using data they do not trust is alarming,” said Craig Stewart, CTO at SnapLogic. “To get data analytics projects right, it’s critical that organisations review what data they have, the applications and sources it comes from and how they are bringing it all together. Modern integration tools can help with this, providing an automated way to democratise data throughout the organisation so it’s accessible at the right time in the right format to all those who need it.”
Despite the data trust gap, analytics is an area that is seeing increased focus and investment during the COVID-19 pandemic, as 66% of organisations surveyed have either continued or even accelerated their warehousing and analytics projects during this period. This seems to indicate that organisations continue to see tremendous value in data-driven insights and are committed to getting analytics right, even or especially in tough times, in order to emerge stronger on the other side.
SnapLogic’s Intelligent Integration Platform uses AI-powered workflows to automate all stages of IT integration projects – design, development, deployment and maintenance – whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments. The platform’s easy-to-use, self-service interface enables both expert and citizen integrators to manage all application integration, data integration, API management, B2B integration and data engineering projects on a single, scalable platform. With SnapLogic, organisations can connect all of their enterprise systems quickly and easily to automate business processes, accelerate analytics and drive transformation.



